The development of wind and solar power capacity has been less in 2016 than in 2015, but even so, the electricity production has slightly increased.

The German Environmental Protection Agency (UBA) has reported that in the first six months of this year the installed capacity of photovoltaic increased by 514 MW, the one of onshore wind by 1683 MW and the one of offshore wind by 269 MW. This means that in comparison to the same period of time last year, 60 percent more wind power was built on land, but 85 percent less offshore wind power, as well as 100 MW less solar power. Figure 1 depicts the capacity additions for the different renewable technologies in a year-on-year comparison.
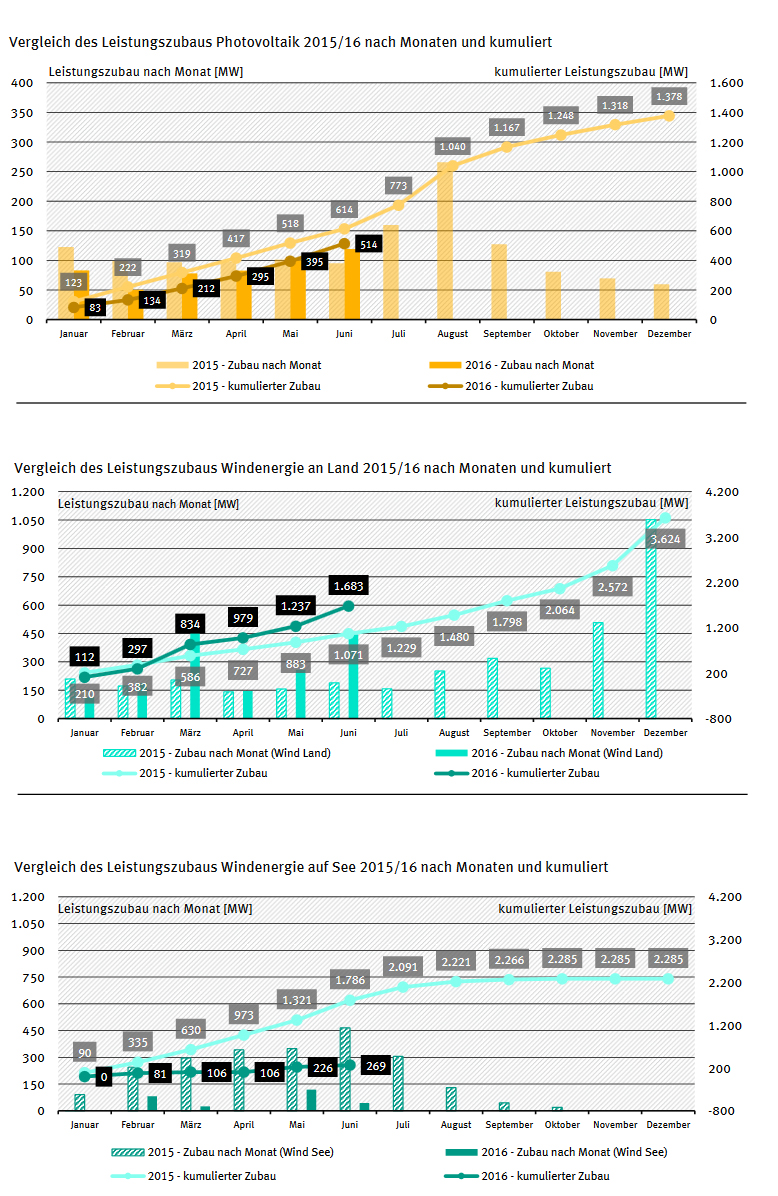
Figure 1: Capacity additions for PV, onshore wind and offshore wind year-on-year comparison (source: Umweltbundesamt)
The production of electricity from solar PV has been less in the first half of 2016 even though the installed capacity has been larger (first half of 2016: 19.4 TWh, first half of 2015: 20.1 TWh). This is partially related to the low amount of direct sunlight in February, March and April of 2016. But in comparison to solar, the amount of electricity produced from wind energy has increased by 8.6 percent, from 37.4 TWh to 40.6 TWh in comparison to last years figures. This increase is thanks to offshore wind power facilities, since bad wind conditions on land for 2016 have led to a slight decrease in power to 34.7 TWh being produced by onshore wind, even though onshore wind power capacities have increased (Source: Montel).
In total, the amount of electricity produced from renewable sources has increased by three percent from 93.7 TWh to 96.6 TWh in compared to the first six months of last year. The power generation of different renewables in the first half of 2015 and 2016 is shown in figure 2.
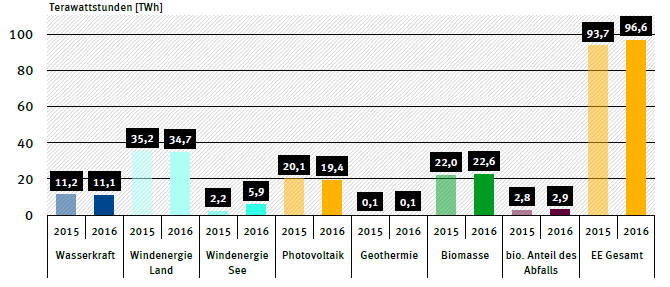
Figure 2: Power generation from renewables in the first half of 2015 and 2016 in TWh (source: Umweltbundesamt)



