The European Commission released a book on the current state of art and opportunities for the Internet of Things (IoT).

The book “Digitising the Industry: Internet of Things Connecting the Physical, Digital and Virtual Worlds” provides insights into the state of the art for research and innovation regarding the Internet of Things (IoT), while exposing you to the challenges and opportunities within the future IoT ecosystems. IoT is considered to be one of the enablers of the next industrial revolution. It is fuelled by the advancement of digital technologies, as well as dramatically changing how companies engage in business activities and people interact with their environment. The IoT’s disruptive nature requires the assessment of the requirements for its future deployment across the digital value chain in various industries and many application areas. The IoT is bridging the physical, digital, cyber and virtual worlds.
The European policy for IoT focusses on three main pillars:
- The creation of a single market for the IoT to guarantee seamless connection among IoT devices and services within the EU
- The support of IoT Ecosystems, where platforms should help to build up a thriving industry around new products and services
- Human-centred IoT that includes the design of IoT applications for empowering citizens while ensuring high privacy and security standards.
The expansion of renewable energy and the decentralization of power generation create great potentials for applying IoT technologies. Smart Grids that allow flexible reaction to power fluctuations is consequently needed. IoT technology can help to pool and control power sources (generation, storage) and sinks (load, storage). IoT devices might then be able to manage the distribution of electricity based on real-time data and situational availability. Figure 1 depicts the interconnections of such a smart grid concept.
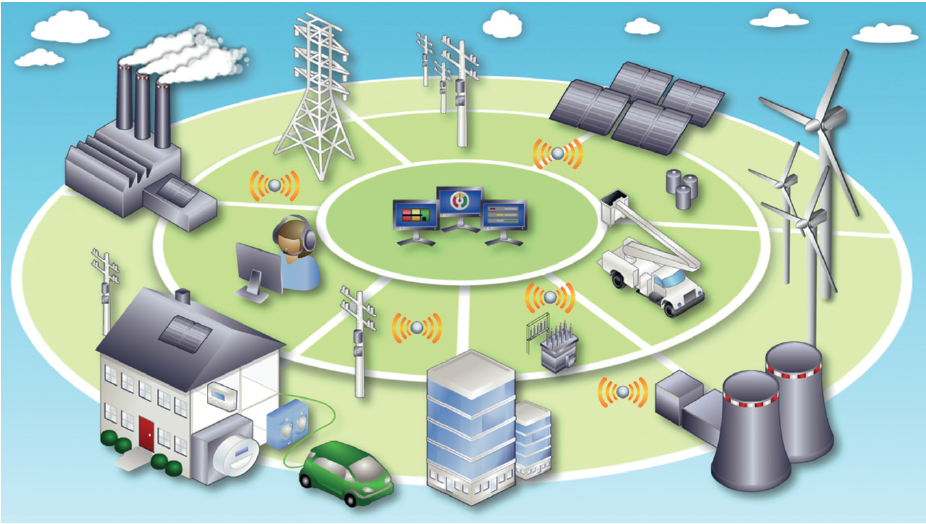
Figure 1: Smart Grid concept (source: River Publishers/European Commission)
International cooperation in the field of IoT is also playing an important role. Especially, the joint development and cooperation with China has been addressed in the EU-China Joint White Paper on the Internet of Things.
In China, the Internet of Things has become an important carrier for strategic information industries and integrated innovation. The central government and local authorities have consistently attached great importance to IoT through the Inter-Ministerial Joint Conference and the ten action plans for IoT development. China’s IoT development now shows a strong momentum. In 2014, China’s IoT industry expanded beyond 620 billion yuan, with a year-on-year growth of 24% . The M2M (machine-to-machine) terminals in China exceeded 73 million units, with a year-on-year growth of 46%, accounting for 30% of the global total. Beijing-Tianjin, Shanghai-Wuxi, Shenzhen- Guangzhou, and Chongqing-Chengdu form the four core industry clusters with unique features and a number of leading enterprises have emerged there. Moreover, IoT third party operation service platforms are rising in traffic, security, health care, energy-saving.
Common challenges for building successful IoT ecosystem have been identified as well. Business models and new ways of cooperation, the interoperability between IoT devices and services, the technical environment and standardization, along with issues of trust and how to integrate IoT in the societal environment are the most important points.



